What is a Virtual Private Network (VPN)?
A VPN or Virtual Private Network is a network connection that enables you to create a secure connection over the public Internet to private networks at a remote location. With a VPN, all network traffic (data, voice, and video) goes through a secure virtual tunnel between the host device (client) and the VPN provider’s servers, and is encrypted. VPN technology uses a combination of features such as encryption, tunneling protocols, data encapsulation, and certified connections to provide you with a secure connection to private networks and to protect your identity.VPN connections technically give you all the benefits of a Local Area Network (LAN), which is similar to that found in many offices but without requiring a hard-wired connection.
Early VPNs were often set up to give individual employees secure remote access to their company networks, hence the name “virtual private network”. By connecting to the company’s network, an individual employee can access all the company’s resources and services as if the employee were inside the company.
Since then, VPNs have evolved to provide the same level of secure communication between any device on the internet. Today, using VPN is increasingly popular among consumers as a means to protect their privacy online, secure their browsing sessions, and get unrestricted access to content or websites that are otherwise blocked or censored.
Types of VPNs
VPNs differ by architecture, purpose of usage, and accessibility. Two basic types of accessibility are site-to-site VPN and remote access VPN.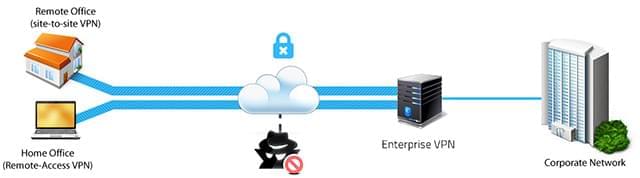 Figure 1. Site-to-Site VPN and Remote Access VPN connecting to a Corporate Network
Figure 1. Site-to-Site VPN and Remote Access VPN connecting to a Corporate NetworkSite-to-site VPNs are used in the corporate environment. A site-to-site VPN ensures the safe encrypted connection of two or more local area networks (LANs) of the same company or of different companies. It means two geographically separated offices are virtually bridged together into a single LAN and users can access data throughout this network.
Remote Access VPNs connect an individual computer to a private network. This type of VPN can be divided again into two groups:
- Corporate VPNs – Corporate VPNs allow business travelers and telecommuters to connect to their company networks and remotely access resources and services on the networks. When a user connects his/her device to the company’s VPN, the VPN thinks that the user’s computer is on the same local network as the VPN.
- Personal VPNs – Personal VPNs provide consumers with the same private and secure connection as the corporate VPNs. However, personal VPNs are not used to connect to private networks to access private resources.
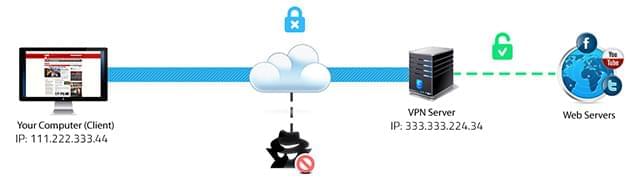
Personal VPN services are especially useful when connecting to a public WiFi network. It is estimated that nearly 90% of public WiFi networks are not secured. By using a VPN service, all your internet communications will be encrypted, making it almost impossible for hackers and snoopers to read and steal your private information.
There are many personal VPN service providers available for consumers to choose from, with many offering VPN services to consumers for free or for a low monthly subscription fee. These services also make it easy and quick for you to install and use a VPN on practically any platform, including mobile and tablet devices.
Benefits of Masking Your IP Address
A VPN masks your IP address, giving you much greater privacy for your online activities. Unshielded, this IP address – the unique address for each device on the internet – can be misused to reveal your identity, location, ISP, and even the specifics of your online activity.When you use a VPN, your IP address is masked so you can surf the web anonymously. Thus, no one can find out where you connect from or what you do online.
Moreover, by exchanging your IP address with the VPN server’s IP address, you can virtually connect from a geographic location that is different from where you are physically located.
For instance, you may be sitting inside a coffee shop in Dubai, but by connecting to a remote VPN server, you can appear to connect to the Internet from another location (i.e. San Francisco or New York) which hosts the VPN server you’re connecting to.
This enables you to bypass regional internet restrictions and get access to content (i.e. YouTube, Facebook) or internet services (i.e. Skype, Gmail, Viber) that are otherwise restricted or censored in the location you are staying in.
VPN Hardware and Software
VPN is a client-server technology that is made up of hardware and software components on both the client (user) side and the server side. As VPNs have progressed from a corporate tool into today’s personal VPN, the installation requires no additional hardware on the user side other than the computer or device for accessing the internet.Client (your computer)
- The hardware is the personal computer, smart phone or tablet
- The software is the VPN client app running on your device
VPN Server
- The hardware are server computers and traffic routers
- The software controls the traffic routing and communication between the servers and the client (your computer).
VPN traffic flow
Both inbound and outbound traffic is routed through VPN servers. Depending on the traffic direction, the data is encrypted and decrypted either on the client’s computer or on the VPN server. For example, let’s assume you want to watch video on YouTube. You search for the video on YouTube and play it. Since this is outbound traffic, this data is encrypted on your computer by the VPN client.Encrypted commands are sent to the closest VPN server, which then forwards the encrypted commands through the network of the servers to the gateway server, where the command is decrypted and sent through the public internet to YouTube.
As the video is played, since it is inbound traffic, the process is repeated in reverse. The video stream goes to the VPN server where it gets encrypted, sent to the closest client server, and forwarded to the client where it is decrypted and played in the client’s internet browser. You, as the user (client), get the IP address of the VPN gateway server so it is difficult to track down your real IP address and pinpoint your geographical location.
Security at the packet level
VPN security begins at the data packet level – the basic building block of online communication. Each data packet is encrypted, packaged in multiple envelopes, and treated as a certified letter. Taken together, these steps ensure data is secure even against deep data packet analysis and potential eavesdropping anywhere between the two connected computers.Encryption
Full data encryption is a basic element in a VPN. With a VPN, all traffic between the two computers is encrypted and isolated in a secure tunnel, shutting out ISPs from eavesdropping and logging your web activity.Encryption for devices connected to a VPN goes beyond just web browsing. It includes VOIP communication, Skype, emails – anything that uses an online connection. This gives you more comprehensive protection than a proxy server, which is limited to only shielding your web browsing activity.
Envelope Strategy
VPNs use various tunneling protocols to encapsulate data packets for secure transit. Tunneling protocols essentially place the individual data packets – open postcards with the names of the sender and recipient and the data payload – into new sealed envelopes marked with the IP address of the VPN. Each envelope contains and conceals the earlier message envelopes. In addition to the layered envelopes, the original message within is also encrypted.Point-to-point Communication
When a VPN tunnel connection is opened up, it authenticates sender identity and the integrity of the sent messages. Similar to a registered letter providing point-to-point communication, it ensures that no unauthorized people can intercept the message and that data packets are not tampered with.VPN Security Protocols
In the pursuit of creating a virtual private network, with its combination of tunneling, encryption, and data encapsulation, security experts have created three different families of VPNs, each with their own specific characteristics: IPsec, PPTP, and SSL. There is no “one-size-fits-all” list of specs for a VPN. Computer experts primarily divide them by technical details and consumers distinguish them by ease of use and portability.IPsec Family
- Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) – With IPsec, all application traffic is secured across an IP network. IPsec protocol provides session authentication and data packet encryption between the two connected parties. It is primarily designed for protecting the data flows between networks (network-to-network) and the individual worker’s remote connection to the company network.
- Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) – L2TP is used to make a tunnel between two L2TP control connection endpoints. Because it does not provide any encryption or authentication features by itself, it is usually paired with an encryption protocol such as IPsec.
PPTP family
Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) uses a point-to-point protocol to make a direct connection between two nodes. It was the first VPN protocol to be supported by Microsoft Dial-up Networking and has been bundled into all releases of Microsoft Windows since Windows 95. The Microsoft connection has been an important part of PPTP’s acceptance in the market.While the PPTP protocol has the advantage of a pre-installed client base on Windows platforms, analysis by cryptography experts have identified several security issues such as its vulnerability to password guessing attacks.
SSL family
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS)
– SSL is commonly used to secure online shopping as a user’s web
browsers can almost transparently switch to SSL without requiring
additional configuration or extra software. SSL was the industry
standard before it evolved into Transport Layer Security. The SSL
protocol works at the application level independent of the specific
network. The “sockets” part of the term refers to the sockets method of
passing data back and forth between a client and a server or program
layers in the same computer.
SSL uses the public-and-private key encryption system from RSA, which also includes the use of a digital certificate. TLS and SSL are an integral part of most Web browsers (clients) and Web servers. - Open VPN – OpenVPN is an open source VPN based on the SSL protocol that is focused on organizations in the SME (Small and Medium Enterprise) and enterprise segment. It provides portability, ease of configuration, and compatibility with NAT (Network Address Translation) and dynamic addresses.



































